Sorts Part 1
Learn and perform Algo Rythmic interpretation of Classes, Queues, performing Sorts.
Algo Rythmics Planning and Coding Week
There is a craze in either Dancing or Algo Rythmic societies to combine Coding and Dancing. Plus, Computer Science at Del Norte needs a traditional activity (aka Physics Boat races)!!! You will be first gneraction to perform. Here are some samples …
This is a two week mini project containing Sorting Code and Algo Rythmic performance of your favorite algorithm. Have fun and don’t be afraid to be creative.
Information about Selection Sort, Insertion Sort, Merge Sort
For the AP exam, there are three main sort algorithms you will need to know and be able to use fluently: insertion, merge, and selection sort.
-
Selection Sort Lecture on Arrays/ArrayLists
Selection sort is a linear sort algorithm as it moves from index [0] to [n-1]. In the inner loop which is a second linear loop it compares two elements (like seen in the visual below) and notes which is smallest, after cycling to the end it swaps the smallest number to beginning position in the round.
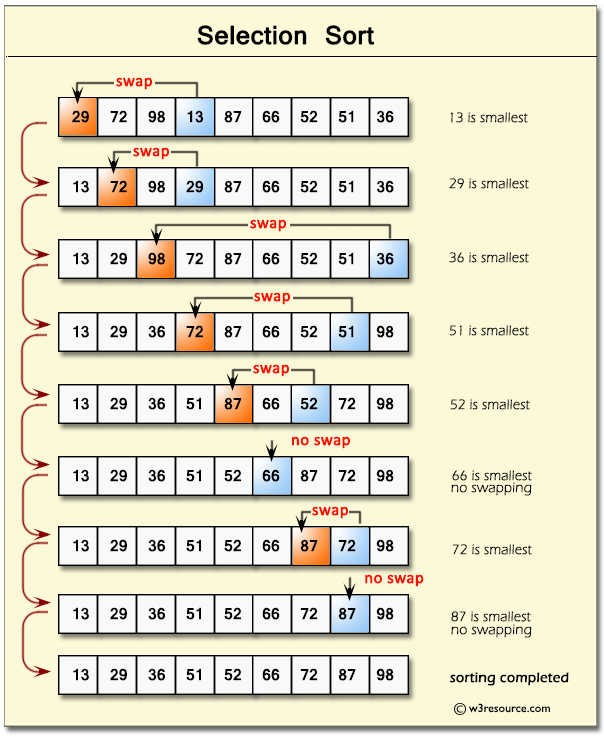
-
Insertion Sort Lecture on Arrays/ArrayLists – Sample code that Sorts Objects
Insertion sort is another linear algorithm that sorts elements from index [0] to index [n-1]. In the inner loop of this algorithm, it finds the gap, insertion point for the next item and inserts it. Each inner loop leave the list partially sorted according to outer loops index.
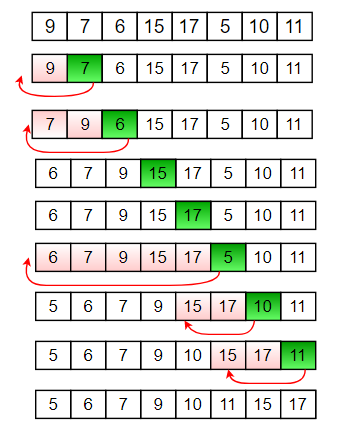
-
Merge Sort Algorithm part 1, Algorithm part 2
This algorithm uses a divide and conquer algorithm, versus linear algorithm of insertion or selection sort. Looking at it can be complicated, but it is more simple than it looks. It divides the array into two different groups recursively, until it gets only two to compare, swaps if necessary. Then it pops out of the recursion, observe the cascading and then the inverted assembly in illustration, after pop it puts each split group back together using a sorted comparison.

import java.util.Arrays;
public class TQueue<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private Node<T> front;
private Node<T> rear;
private int size;
public TQueue() {
front = null;
rear = null;
size = 0;
}
// Node class to represent elements of the queue
private static class Node<T> {
T data;
Node<T> next;
Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Method to add an item to the queue
public void enqueue(T item) {
Node<T> newNode = new Node<>(item);
if (isEmpty()) {
front = newNode;
} else {
rear.next = newNode;
}
rear = newNode;
size++;
}
// Method to remove and return the first item from the queue
public T dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue is empty");
}
T item = front.data;
front = front.next;
if (front == null) {
rear = null;
}
size--;
return item;
}
// Method to check if the queue is empty
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// Method to print the elements of the queue
public void printQueue() {
Node<T> current = front;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Method to perform bubble sort on the queue
public void bubbleSort() {
if (size <= 1) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
Node<T> current = front;
Node<T> nextNode = front.next;
for (int j = 0; j < size - i - 1; j++) {
if (current.data.compareTo(nextNode.data) > 0) {
T temp = current.data;
current.data = nextNode.data;
nextNode.data = temp;
}
current = nextNode;
nextNode = nextNode.next;
}
}
}
// Method to perform selection sort on the queue
public void selectionSort() {
if (size <= 1) {
return;
}
Node<T> current = front;
while (current != null) {
Node<T> min = current;
Node<T> nextNode = current.next;
while (nextNode != null) {
if (nextNode.data.compareTo(min.data) < 0) {
min = nextNode;
}
nextNode = nextNode.next;
}
T temp = current.data;
current.data = min.data;
min.data = temp;
current = current.next;
}
}
// Method to perform insertion sort on the queue
public void insertionSort() {
if (size <= 1) {
return;
}
Node<T> current = front.next;
while (current != null) {
T key = current.data;
Node<T> prev = current;
Node<T> temp = front;
while (temp != current) {
if (temp.data.compareTo(key) > 0) {
prev.next = current.next;
current.next = temp;
if (temp == front) {
front = current;
} else {
prev.next = current;
}
break;
}
prev = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
current = current.next;
}
}
// Method to get the tail node of the queue
private Node<T> getTail(Node<T> node) {
while (node != null && node.next != null) {
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
// Method to perform quick sort on the queue
public void quickSort() {
if (front == null) {
return;
}
Node<T> end = getTail(front);
front = quickSort(front, end);
}
// Recursive method for quick sort
private Node<T> quickSort(Node<T> start, Node<T> end) {
if (start == end || start == null || start.next == end) {
return start;
}
Node<T> pivot = partition(start, end);
pivot.next = quickSort(pivot.next, end);
if (pivot == start) {
return pivot;
}
Node<T> temp = start;
while (temp.next != pivot) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = pivot;
return start;
}
// Method to partition the queue for quick sort
private Node<T> partition(Node<T> start, Node<T> end) {
if (start == end || start == null || start.next == end) {
return start;
}
T pivotValue = end.data;
Node<T> pivot = start;
Node<T> current = start;
while (current != end) {
if (current.data.compareTo(pivotValue) < 0) {
T temp = pivot.data;
pivot.data = current.data;
current.data = temp;
pivot = pivot.next;
}
current = current.next;
}
T temp = pivot.data;
pivot.data = end.data;
end.data = temp;
return pivot;
}
// Method to perform merge sort on the queue
public void mergeSort() {
front = mergeSort(front);
}
// Recursive method for merge sort
private Node<T> mergeSort(Node<T> head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
Node<T> middle = getMiddle(head);
Node<T> nextOfMiddle = middle.next;
middle.next = null;
Node<T> left = mergeSort(head);
Node<T> right = mergeSort(nextOfMiddle);
return merge(left, right);
}
// Method to find the middle node of the queue
private Node<T> getMiddle(Node<T> head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
Node<T> slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
// Method to merge two sorted queues
private Node<T> merge(Node<T> left, Node<T> right) {
if (left == null) {
return right;
}
if (right == null) {
return left;
}
Node<T> result;
if (left.data.compareTo(right.data) <= 0) {
result = left;
result.next = merge(left.next, right);
} else {
result = right;
result.next = merge(left, right.next);
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TQueue<Integer> intQueue = new TQueue<>();
// Adding elements to the queue
intQueue.enqueue(3);
intQueue.enqueue(1);
intQueue.enqueue(4);
intQueue.enqueue(1);
intQueue.enqueue(5);
intQueue.enqueue(7);
intQueue.enqueue(2);
System.out.println("Before sorting:");
intQueue.printQueue();
// Testing the different sorting algorithms
intQueue.bubbleSort();
System.out.println("After sorting with Bubble Sort:");
intQueue.printQueue();
intQueue.selectionSort();
System.out.println("After sorting with Selection Sort:");
intQueue.printQueue();
intQueue.insertionSort();
System.out.println("After sorting with Insertion Sort:");
intQueue.printQueue();
intQueue.quickSort();
System.out.println("After sorting with Quick Sort:");
intQueue.printQueue();
intQueue.mergeSort();
System.out.println("After sorting with Merge Sort:");
intQueue.printQueue();
}
}
TQueue.main(null);
Before sorting:
3 1 4 1 5 7 2
After sorting with Bubble Sort:
1 1 2 3 4 5 7
After sorting with Selection Sort:
1 1 2 3 4 5 7
After sorting with Insertion Sort:
1 1 2 3 4 5 7
After sorting with Quick Sort:
1 1 2 3 4 5 7
After sorting with Merge Sort:
1 1 2 3 4 5 7